Activated carbon is a highly adsorptive material characterized by its large surface area and well-developed pore structure. It is widely used in water treatment, air purification, gold extraction, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries.
While many people are familiar with the uses of activated carbon, few understand how it is made. This article takes you through the entire production process — from raw material selection to final packaging.
Raw Material Selection: Quality Determines Performance
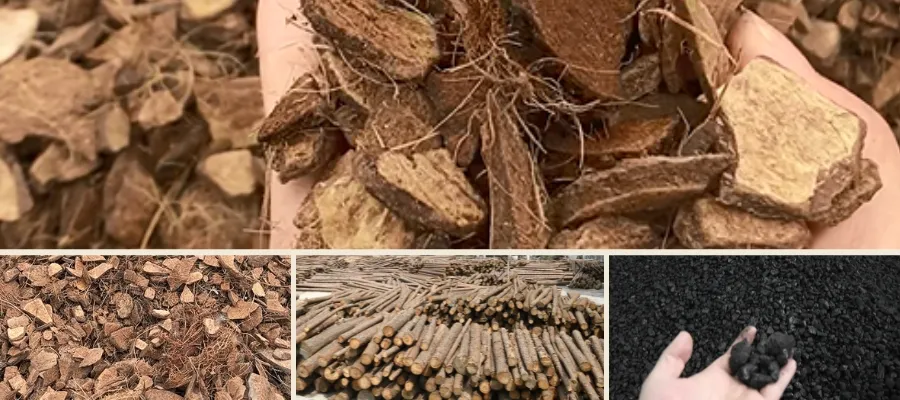

The performance of activated carbon largely depends on the raw materials used. Common raw materials include:
- Coconut shell: Known for high hardness, low ash content, and a predominantly microporous structure. Ideal for drinking water purification and gold recovery.
- Coal: Including anthracite and bituminous coal, which are suitable for producing high-strength, abrasion-resistant activated carbon. Commonly used in gas purification, solvent recovery, and industrial water treatment.
- Wood: Features a highly developed pore structure and large surface area, suitable for decolorization, purification, and gas adsorption.
Different raw materials produce different pore structures after carbonization and activation, allowing them to meet diverse industrial requirements.
Raw Material Preparation
Before production begins, the raw materials undergo cleaning, drying, and crushing to remove impurities and control particle size, ensuring processing efficiency and consistent product quality.
Contact me todayCarbonization: From Organic Matter to Carbonaceous Material
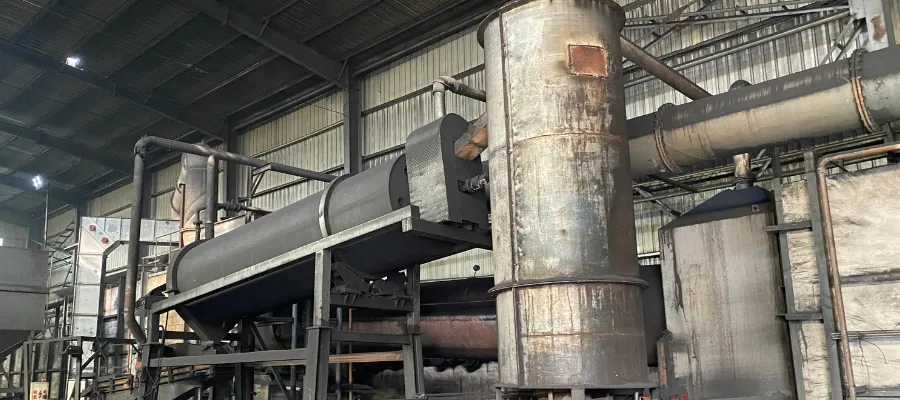

Once prepared, the raw materials enter the carbonization stage.
Purpose of Carbonization
Carbonization involves heating the raw material in a low-oxygen or oxygen-free environment (around 400°C–800°C) to remove non-carbon elements (such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen), leaving behind a solid carbon-rich material.
Carbonization Process
- Heating: The raw material is gradually heated in a carbonization furnace to avoid rapid decomposition.
- Decomposition: At high temperatures, organic compounds decompose into gases (e.g., water vapor, methane, and carbon dioxide) and solid carbonaceous material.
- Cooling: After carbonization, the material is slowly cooled to room temperature, resulting in a semi-finished carbonized product.
Activation: Developing the Pore Structure
Activation is the most critical step in determining the performance of activated carbon. The goal is to use gas or chemical agents to partially oxidize and etch the carbonized material, forming a network of micro-, meso-, and macropores. There are two main activation methods:
Physical Activation
This method uses steam or carbon dioxide at high temperatures (800–1000°C) to react with the carbonized material. The partial oxidation creates pores and increases surface area.
Physical activation is typically used for coconut shell and coal-based activated carbon, producing products with high strength and excellent adsorption performance.
Chemical Activation
In this method, chemical reagents such as potassium hydroxide (KOH), phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄), or zinc chloride (ZnCl₂) are added before or during carbonization.
These chemicals promote pore development through dehydration and oxidation at relatively lower temperatures. Chemical activation is often applied to wood-based activated carbon, resulting in materials with a highly developed pore structure and outstanding adsorption capacity.
Contact me todayCrushing and Sieving: Determining Particle Size and Form
After activation, the carbon material is crushed and sieved to achieve the desired particle size and form. Common forms include:
- Granular Activated Carbon: Used in water treatment, solvent recovery, and air purification.
- Cylindrical (Pellet) Activated Carbon: Cylindrical in shape, ideal for gas purification and emission control.
- Powdered Activated Carbon: Fine powder used for decolorization, purification, and batch treatment processes.
Each form of activated carbon serves specific applications and performance requirements.
Washing and Drying: Removing Impurities and Moisture
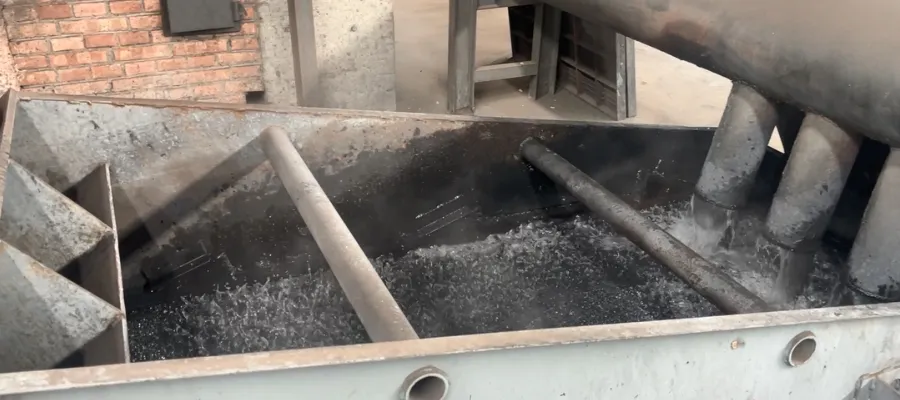

Even after activation, the product may contain ash, residual chemicals, or soluble impurities. Therefore, washing (acid washing or water washing) is essential to:
- Reduce ash content;
- Adjust and stabilize pH levels;
- Improve purity and consistency.
After washing, the activated carbon is dried to remove excess moisture, ensuring stable performance during storage and transportation.
Testing and Quality Control: Ensuring Performance Compliance
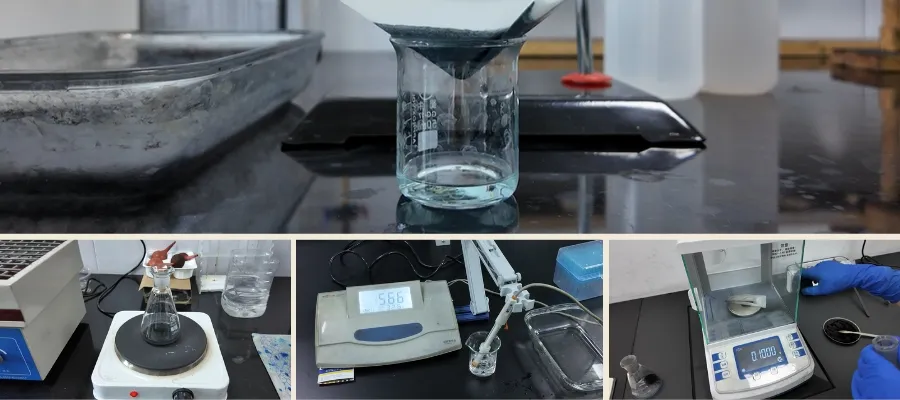

Finished activated carbon must undergo strict quality testing. Common test parameters include:
- Iodine Number: Indicates micropore development;
- CTC Adsorption: Reflects mesopore adsorption capacity;
- Surface Area: A key indicator of adsorption potential;
- Hardness: Measures resistance to abrasion and breakage;
- Ash and Moisture Content: Assess overall purity and stability.
These parameters provide a comprehensive evaluation of activated carbon’s performance and application suitability.
Contact me todayPackaging and Storage: Ensuring Safe Delivery
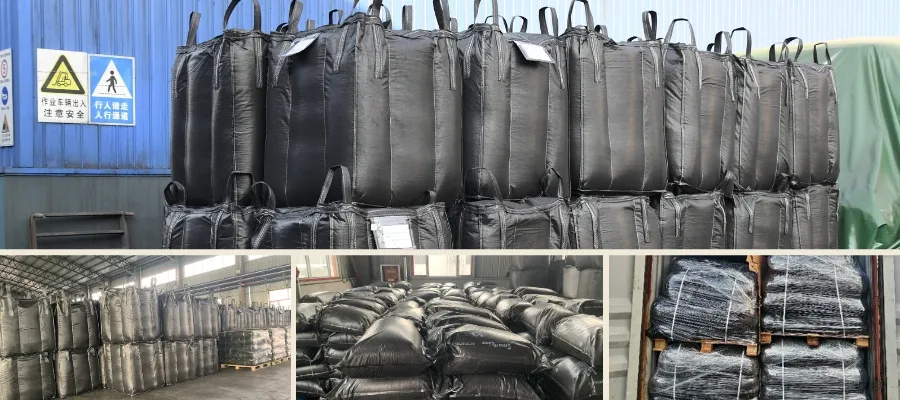

Qualified activated carbon products are packed using automated systems into moisture-proof bags, such as 25 kg or 500 kg jumbo bags, or customized packaging. During storage and transportation, they must be kept dry, away from open flames, and protected from airborne contaminants that could affect performance.
Environmental Protection and Recycling
Activated carbon production generates exhaust gases, wastewater, and solid residues, making environmental management a vital part of the process:
- Gas Treatment: Adsorption towers capture volatile organic compounds and fumes.
- Wastewater Treatment: Chemical activation wastewater must be neutralized and filtered before discharge.
- Recycling: Spent activated carbon can often be regenerated and reused, extending its service life and reducing waste.
Conclusion
The production of activated carbon is a complex and precise process. Every step — from raw material selection to final packaging — influences the quality and performance of the end product. Through a well-controlled production process, manufacturers can enhance adsorption capacity while minimizing environmental impact.
As a professional activated carbon supplier, TingyuanCarbon produces a wide range of high-quality activated carbon products, offering customized solutions for various industrial applications.
Contact us today for free sample testing and competitive pricing.