Biogas is a vital renewable energy source produced through anaerobic fermentation of organic materials such as agricultural waste, food scraps, and sludge. Its primary components are methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂), though it also contains trace amounts of harmful impurities including hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), siloxanes, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and ammonia (NH₃).
Before utilizing biogas as a clean fuel or upgrading it to renewable natural gas (RNG), these impurities must be removed. Activated carbon plays a critical role in this purification process.
This article explains the role of activated carbon in biogas purification, helping you make informed decisions for your biogas treatment needs.
Sources and Impacts of Biogas Contaminants
The contaminants in biogas mainly originate from the feedstock characteristics and the anaerobic digestion process. Understanding their sources and effects is essential for designing an efficient purification system.
- Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S): Produced from the decomposition of sulfur-containing organic matter such as proteins and sludge. H₂S is highly corrosive and toxic — even trace amounts can damage engines, turbines, and pipelines, shortening equipment lifespan and posing safety risks.
- Siloxanes: Derived primarily from personal care products, lubricants, and detergents. When burned, siloxanes form silicon dioxide (SiO₂) deposits that adhere to equipment surfaces, reducing efficiency and increasing maintenance costs.
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): Generated by the breakdown of organic waste; some, such as benzene and toluene, are harmful to human health and affect the odor and quality of biogas.
- Ammonia (NH₃): Originates from nitrogen-rich materials like manure and food residues. High concentrations of ammonia can corrode equipment and reduce combustion efficiency.
Removing these contaminants is essential for ensuring biogas quality, extending equipment lifespan, and meeting emission standards.
The Role of Activated Carbon in Biogas Purification
Activated carbon is a highly effective adsorbent with a well-developed pore structure and extremely large surface area. It can capture and remove a wide range of harmful impurities from biogas, including sulfur compounds, organic vapors, siloxanes, and ammonia. The purification mechanism involves both physical and chemical adsorption:
- Physical adsorption: Relies on the van der Waals forces between molecules to trap impurities within the micro-, meso-, and macropores of activated carbon. Micropores are ideal for small molecules (e.g., H₂S), while meso- and macropores capture larger organic molecules or siloxanes.
- Chemical adsorption: Utilizes surface functional groups or impregnated chemicals (such as KI or KOH) that react with contaminants, permanently removing them and enhancing adsorption capacity and efficiency.
In biogas treatment, activated carbon is typically installed in fixed-bed adsorption systems. Raw biogas enters from the bottom of the tower, passes through the carbon bed where impurities are adsorbed, and exits as purified gas from the top.
Key advantages of this process include:
- Continuous operation: Once the carbon bed is saturated, the media can be replaced or regenerated without significant downtime.
- Stable efficiency: Works effectively at ambient temperature and pressure, without complex operational requirements.
- High adaptability: Different types of activated carbon (impregnated or non-impregnated) can be selected based on gas composition, contaminant concentration, and humidity.
Types of Activated Carbon for Biogas Purification
Selecting the right type of activated carbon is critical for optimal purification performance. Tinyuancarbon provides high-quality activated carbon for biogas purification, significantly improving biogas utilization efficiency.
Pelletized Activated Carbon
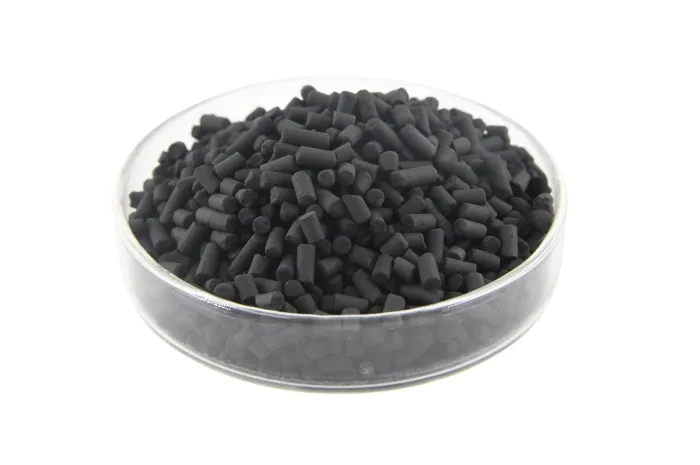

Produced from high-grade coal through crushing, molding, carbonization, and activation processes. Its cylindrical shape, high mechanical strength, and low pressure drop make it ideal for continuous fixed-bed systems.
Key Features:
- Low pressure drop: The uniform shape and high strength minimize resistance during gas flow, reducing energy consumption.
- High abrasion resistance: Performs excellently under high flow conditions or in systems requiring frequent replacement, reducing dust formation.
- High surface area and excellent adsorption: The uniform pore structure enables effective adsorption of hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), siloxanes, and VOCs. Its high capacity extends service life and lowers operational costs.
Applications:
Pelletized activated carbon is commonly used to treat biogas with high H₂S concentrations, particularly in large industrial fixed-bed systems.
Granular Activated Carbon
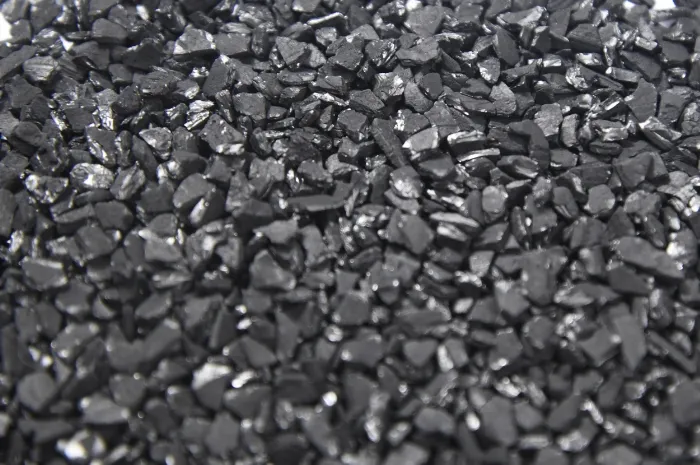

We produce 4×10 mesh granular activated carbon specifically for biogas purification. Its porous structure and large surface area provide exceptional adsorption performance while maintaining operational flexibility.
Key Features:
- Versatile: Suitable for multiple system types, including fixed-bed and fluidized-bed units.
- High adsorption capacity: Effective for biogas containing complex mixtures of contaminants, such as H₂S, siloxanes, and VOCs.
- Easy handling: Simple to load and replace, ideal for systems requiring frequent maintenance.
Applications:
Granular activated carbon is widely used in small and medium-sized biogas purification systems — such as kitchen waste biogas plants and medium-scale landfill gas purification facilities — where flexibility is needed.
Impregnated Activated Carbon
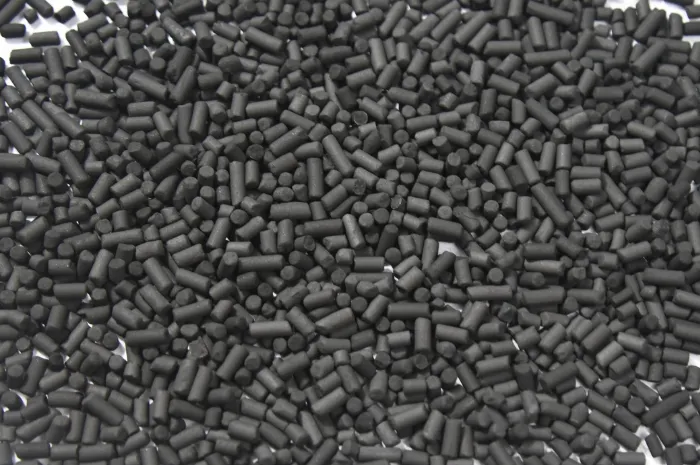

Impregnated activated carbon is treated with chemical agents (e.g., alkaline substances or oxidants) to enhance its adsorption capacity for specific gases. It is specially designed to remove corrosive gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) and ammonia (NH₃) from biogas.
Key Features:
- High desulfurization efficiency: Chemically reacts with H₂S to convert it into elemental sulfur or sulfates, achieving deep desulfurization.
- Large adsorption capacity: Can remove 2–5 times more sulfur compounds than non-impregnated carbon.
- Fast reaction rate: Maintains high efficiency even at low temperatures.
- Long service life: Operates stably for extended periods under well-controlled humidity and temperature conditions.
Applications:
Ideal for high-sulfur biogas desulfurization and gases containing both ammonia and sulfur oxides.
Conclusion
Activated carbon plays a vital role in biogas purification, effectively removing hydrogen sulfide, siloxanes, VOCs, and other harmful impurities to convert raw biogas into a clean, renewable energy source.
TingyuanCarbon offers a wide range of high-performance activated carbon products with excellent adsorption efficiency and superior mechanical strength, suitable for all types of biogas purification systems.
Contact us today for more information or to request a quotation.