Industrial odor issues not only affect the working environment but may also trigger complaints from nearby residents, directly impacting business sustainability. From food processing and chemical plants to waste treatment stations, odor control has become a key indicator of environmental compliance.
As an efficient adsorbent material, activated carbon plays a crucial role in odor control. This article provides comprehensive reference for professional clients from technical principles to applications and product selection.
Sources and Hazards of Industrial Odors
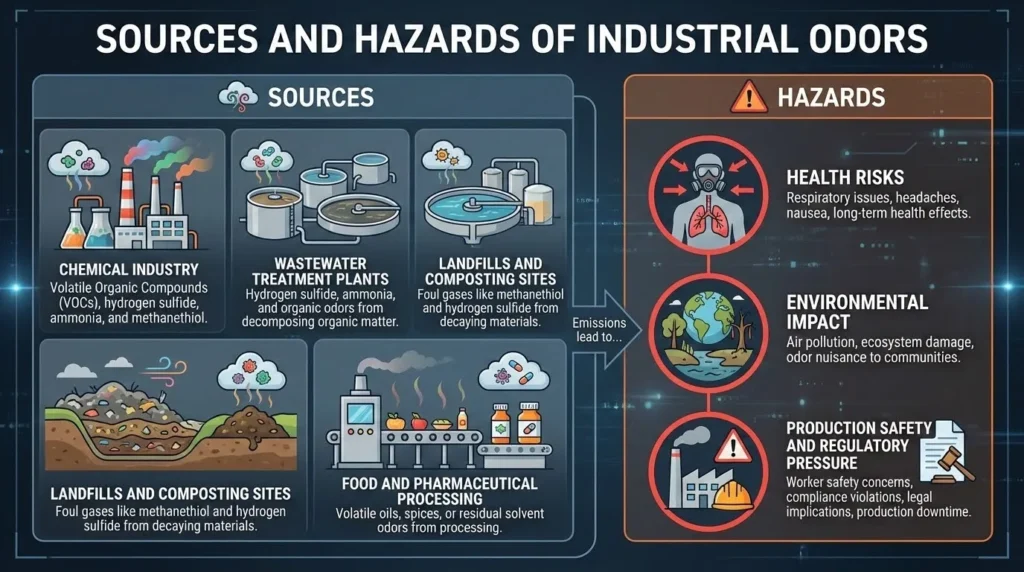
In industrial environments, odor issues are particularly prominent, with complex sources and various types that may pose environmental and health risks:
Main Sources
- Chemical Industry: Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and methanethiol.
- Wastewater Treatment Plants: Hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and organic odors from decomposing organic matter.
- Landfills and Composting Sites: Foul gases like methanethiol and hydrogen sulfide from decaying materials.
- Food and Pharmaceutical Processing: Volatile oils, spices, or residual solvent odors from processing.
Hazards
- Health Risks: Prolonged exposure to odorous gases may cause headaches, nausea, respiratory irritation, or chronic diseases.
- Environmental Impact: Some VOCs and sulfur compounds are pollutants affecting air quality.
- Production Safety and Regulatory Pressure: Excessive industrial odor emissions may violate environmental regulations, leading to fines or production restrictions.
Therefore, using activated carbon for odor control is crucial for industrial environmental safety and compliance.
Contact me todayPrinciples of Activated Carbon Odor Control
Activated carbon controls odors through two main mechanisms:
Physical Adsorption
- Activated carbon pores provide enormous surface area, adsorbing odor molecules through Van der Waals forces.
- Highly effective for common VOCs, hydrocarbons, smoke, and kitchen oil fumes.
Chemical Adsorption
- Regular physical adsorption has limitations for sulfur-containing, nitrogen-containing, or corrosive gases.
- Through surface chemical modification (such as sulfur impregnation, metal oxide doping, amine treatment), activated carbon can chemically react with odor molecules for long-term removal.
In professional applications, selecting appropriate types and modification processes of activated carbon is crucial for different odor sources.
Activated Carbon Selection Guide for Odor Control
Selecting the appropriate activated carbon is critical based on the odor source, gas concentration, and treatment method. Below are common types and application recommendations:
Granular Activated Carbon
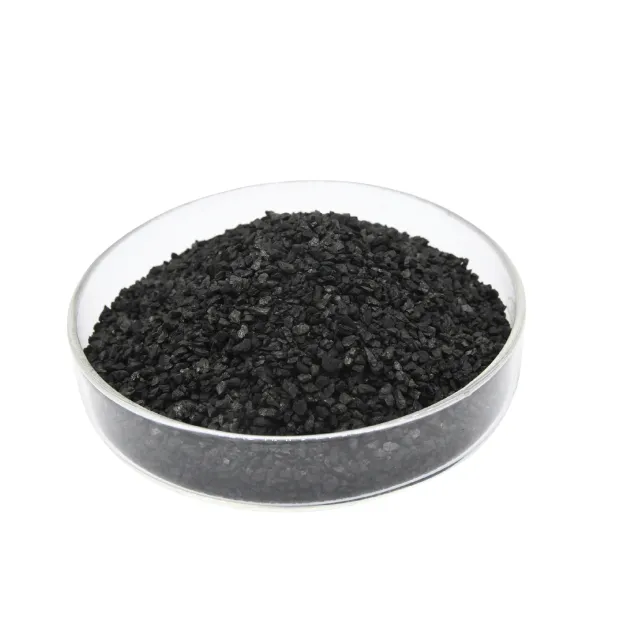

- Features: Uniform particles, high mechanical strength, good wear resistance, can withstand gas flow erosion.
- Applications: Industrial waste gas treatment, air filters, ventilation duct purification.
- Advantages: Large adsorption capacity, recyclable, stable long-term operation.
Pellet Activated Carbon
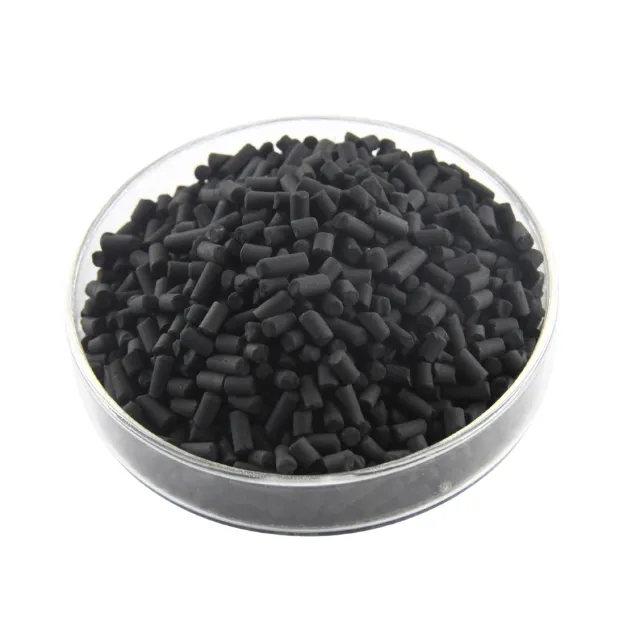

- Features: Cylindrical particles, uniform pore distribution, low pressure drop, high flow rate tolerance.
- Applications: Suitable for continuous industrial waste gas treatment systems, adsorption towers, or bed layer filling.
- Advantages: Low gas passage resistance, high adsorption efficiency, suitable for high flow rate or high concentration gases.
Impregnated Activated Carbon

- Features: Surface impregnated with metal oxides or chemical functional groups (copper, zinc, amino, sulfur) to enhance adsorption and chemical reaction with specific odor molecules.
- Applications: Suitable for industrial treatment of hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), ammonia (NH₃), methanethiol, and other malodorous gases.
- Advantages: High specificity, high removal rate, significant long-term performance.
Selection Guidelines:
- Small odor molecules, medium concentration → Granular activated carbon
- High flow rate or continuous waste gas → Pellet activated carbon
- Special malodorous gases (H₂S, NH₃, etc.) → Impregnated activated carbon
Precautions for Using Activated Carbon
- Regular replacement or regeneration: Effectiveness decreases when adsorption reaches saturation
- Humidity control: High humidity affects adsorption performance
- Proper configuration: Choose appropriate quantity based on space volume and odor concentration
Conclusion
Odor control is a systematic project, and selecting suitable activated carbon is just the first step. TingyuanCarbon provides one-stop services from technical consultation to customized products, helping enterprises establish long-term odor control systems.
Please feel free to contact us for detailed technical materials or sample testing requests.





